Technology Trends

Location-based analytics is an extra layer of geographical data for your business. Mapsted Location-based data analytics allow you to extract more valuable insights, allowing you to gain a deeper understanding of your consumers’ or staff’s activities. People also call it “geo-analytics”. Across industries such as higher education, big-box retail, shopping malls and transportation hubs, business data, including data on people, transactions, events, assets and more, often includes a geographic component. When added to an analysis of performance, location-based analytics can unlock new related insights. This allows for greater context when asking questions about how your business processes, offering a new understanding of trends and relationships in the data.
How is Location-Based Analytics Helpful?
Location-based data analytics provides everyone in an organization with spatial analytics and other analytics capabilities to understand the data through a location-specific perspective, make predictions and optimize business practices accordingly. Organizations add location to their analytics to provide greater context in decision-making and uncover deeper insights that traditional, flat business intelligence (BI) data might miss.
Furthermore, Mapsted’s Maps uniquely generate insights from location data and make them especially easy for non-experts to understand. This would not be possible with traditional analytics such as statistical plots, charts or tables. From optimizing operations across different territories to matching assets in the field to appropriate resources to testing the profitability of potential new locations, location analytics can help businesses make better decisions based on geospatial information.


What are the Benefits of Location-Based Analytics?
In today’s global economy understanding geospatial impacts on the business is critical for success. Companies that use location analytics to assess their business strategies can decrease costs, locate new sales opportunities, and implement changes for operational efficiency. Furthermore, location analytics is highly visual and therefore easier for non-experts to understand insights found in the data. This enables teams across the organization to communicate insights and act on them more easily.
The following are 3 ways your business can greatly benefit from implementing location-based analytics:
1. Hyperlocal intelligence
With location analytics, you can automatically turn data into location-based insights with beautiful, location-aware visualizations, such as heat maps, and communicate with business users, analysts, scientists, and developers—everyone. This improved information management enhances collaboration across teams and helps everyone in the business make more informed decisions, often leading to reduced costs and increased revenue.
2. Real-World Context
Unlike many other information visualizations, Mapsted Maps connect data to the real world, clearly showing how location relates to other data features. This context enriches insights obtained as analytics teams and end-users drill down into visualizations. It’s often the best way to add context and answer questions related to “where.” This greater context can help organizations find new opportunities and optimize operations.
3. Actionable insights
Mapsted’s Location analytics enables users to create insightful geographical analysis instantly without the learning curve of other tools. But, don’t worry, it still provides the depth of analytical capabilities needed for predictive analysis and other optimizations through the location. It’s the best of both worlds.
How do Various Industries Use Location-Based Analytics?
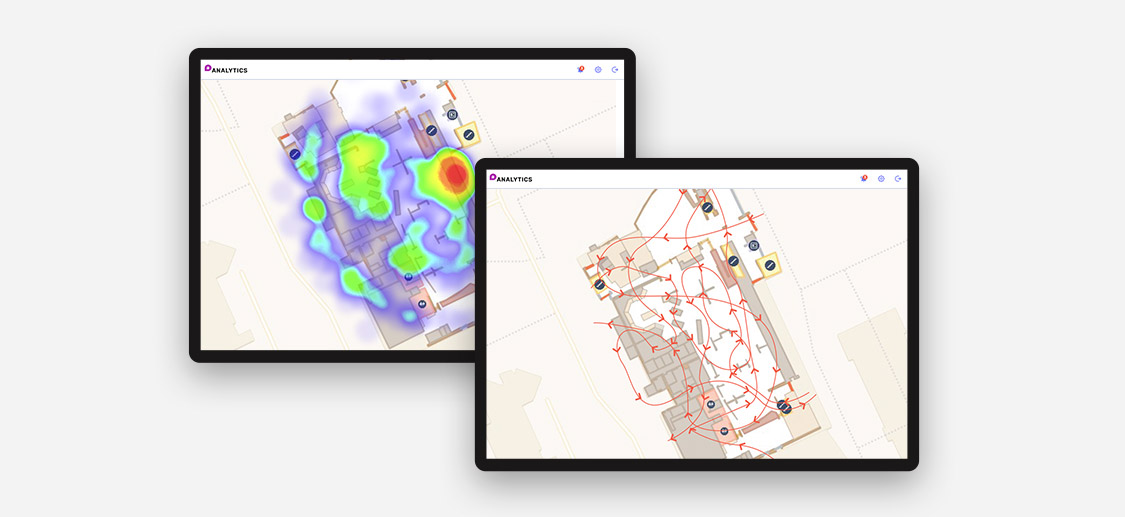
- Businesses can apply location analytics across a variety of industries to drive improvements. In fact, location analytics can help to improve business processes from beginning to end, including manufacturing, assembly, logistics and distribution processes. It can also help improve marketing strategies by using geographical data to better target the right people, make relevant offers in real-time and understand customers’ biggest needs. Furthermore, targeting customers with personalized content has become increasingly popular.
- Location is often included in most business processes. From every financial transaction to stock transactions to location tracking and more, location is a crucial part of any business’s data. More and more organizations are looking for ways to harness their location data. For example, smart cities, connected vehicles, IoT and smart factories are all recent technology developments that rely on location analytics.
- Businesses use location analytics to identify target areas by filtering through demographic data, optimize resource allocation by analyzing localized needs, and predict future business and market trends using historical and real-time data. As a result, businesses can monitor, analyze and make decisions at the right time in the context of geography.
Location-Based Analytics Use Cases and Examples
Retail Site Selection
Retail site selection has come a long way in the past decade, largely due to advances in location intelligence. Years ago, a detailed traffic analysis might have involved physically surveilling a potential location for hours or days at a time and counting the number of cars in the parking lot or the number of shopping carts coming out of a store.
With advanced location intelligence, retailers can work with dynamic map visualizations that reveal populations and demographic groupings. A high-end clothing retailer, for example, can explore potential new locations in the context of surrounding areas and traffic patterns. Retailers can quickly zero in on high-quality sites by visualizing the catchment area for a potential location.
By overlaying competitor locations on top of that, the retailer can get an even better understanding of the potential profitability of a proposed site.
Finally, a retailer can zoom in on a particular neighborhood to better understand the granular traffic patterns within that neighborhood. If a complementary business at one end of the main thoroughfare is attracting the same target demographic, but without being a direct competitor, it is likely to be a better choice than a similar location at the other end of the street.
Better Merchandising
Retailers can also use location-based business intelligence to better serve customers in a particular catchment area.
By analyzing demographic data in the area, for example, a grocery retailer might learn that there is a high population of East Asian immigrants in a nearby community. This could present an opportunity to better serve that audience by adding specialty food items to the product mix, or by advertising in publications or media outlets that cater to the same audience.
Customer Experience

Location intelligence also presents retailers with an opportunity to link their customer’s online experience with brick-and-mortar stores. By connecting website visits and browsing history to a person’s physical presence in the store, retailers can better understand buyer behavior and address their needs.
Location intelligence provides a link between fragmented and incomplete identities such as phone numbers, email, social, or physical addresses and the transactional data and digital marketing activities associated with that customer.
Performance Management
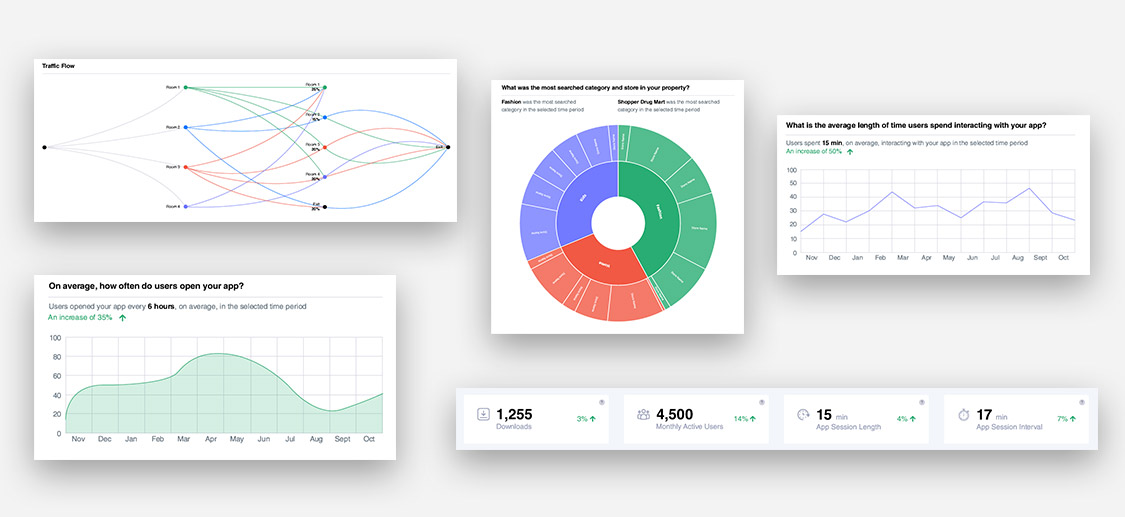
Finally, retailers can use location intelligence to establish better performance benchmarks for individual locations. In many organizations, leaders set annual targets for stores based on a percentage increase over the prior year’s performance.
This tends to challenge high performers, who must constantly strive to exceed last year’s store performance. At the same time, it perpetuates poor outcomes in low-performing stores.
Conclusion
There are several other models for defining performance objectives, each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. If leaders allocate goals based on market opportunity, stores in highly competitive locations may struggle to meet their targets, while those with little competition may achieve them more easily.
With location intelligence, retailers can gain a much richer view of each location’s true profit potential. Retail location-based data analysis affords you the opportunity to understand each location in the context of demographics, traffic, competition, store size and features and more. With location intelligence, store objectives can be defined based on an intelligent analysis of actual profit potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How Mapsted Location-based Analytics Works?
A: Geoanalytics is a method of extracting location-based customer insights from businesses to know every pulse. Information is always crisp, whether it is about customer and staff activities or inventory access. It aids in the analysis of location-specific data to improve prediction and performance.
Mapsted Maps differs from traditional analytics in that it is easier to configure and lacks the technical complexity of a typical analytics tool. Anyone can optimize operations, map field assets, test the profitability of new locations and make firm decisions.
Q2: What is location analytics used for?
A: To closely monitor interactions and infrastructure used in a spatial context, analytics add a geographical layer to map assets, people and infrastructure. Not only that, but insights can be derived to address specific questions and concerns that the organization is facing and insights can be made transparent to stakeholders.
Q3: What type of data is location-based?
A: Geospatial data, also known as location-based business intelligence, adds context to the ecosystem by showing where people and assets are and mapping data points to their behaviour. The most common data types are vector and raster.
Q4: What are the sources of data used by location-based services?
A: Beacons, Wi-Fi and Bluetooth send signals to nearby mobile phones, allowing for the collection of location-based data. This information is then filtered through Mapsted’s analytics tool, which displays footfall, hotspots, time spent in an area and other information.
Q5: Does analytics compromise location privacy?
A: While location analytics for businesses are useful in marketing and decision-making, they do not leave users vulnerable in a tracking environment. The analytics tool does not draw specific information that identifies a specific user, but it does fill in enough information to show how their behavior affects the business’s bottom line.
Q6: How does location-based analytics help businesses?
A: It provides insights into customer behaviour, improves marketing and helps optimize store locations.
Q7: Can small businesses use location analytics?
A: Yes! It helps small businesses understand their customers, plan better and boost sales.
Q8: What industries benefit from location-based analytics?
A: Retail, real estate, healthcare, transportation and hospitality use it to improve services and efficiency.
Q9: How does it enhance customer experience?
A: Location analytics for businesses can work by offering personalized deals, improving navigation and streamlining operations.
Q10: Is location-based analytics safe?
A: Yes, businesses follow privacy laws and use anonymous data to protect user information.
Q11: What is Location-Based Intelligence (LBI)?
A: Location-Based Intelligence (LBI) is the process of collecting, analyzing and visualizing geospatial data to gain insights into patterns, behaviours and trends.
