Museums & Galleries
Today, data has become the most valuable currency because it provides crucial information about customers that businesses need to deliver better experiences. However, obtaining data that is too revealing can be challenging due to various factors. Sometimes, a simple request is sufficient for people to give up their data, while other times it takes more legwork to assure customers that data collection and processing are for their benefit. Regardless, acquiring behavioural data can be costly in terms of productive hours and missed opportunities. This is why big data has become prominent. In this article, we will explore the role museum visitor analytics will play in the future of museums.
To begin, it is important to clarify what big data is not. If you are a small business owner serving customers at a community level, the details on your business database do not constitute big data. However, for a Walmart-like enterprise that handles numerous transactions and segments thousands of complex datasets per minute, such operations fall under the realm of big data.
Key Data Categories that Drive Museum Success
Big Data collected in museums can vary depending on the type of museum and the purpose of data collection. Some common types of Big Data collected in museums are:
- Visitor data: This includes information about visitor demographics, interests, behaviors and feedback.
- Collection data: This includes information about museum objects such as their origin, provenance, condition and usage.
- Operations data: This includes information about museum operations such as budget, staffing, scheduling and maintenance.
- Marketing data: This includes information about the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and advertising efforts.
- Social media data: This includes information about how visitors engage with the museum on social media platforms.

Therefore, big data refers to the vast amount of data generated from human interactions on an hourly or daily basis that impacts businesses. In the context of museums, this data can include visitor numbers, dwell time, traffic hotspots, social media activity (tweets, likes, shares) and more. Such data are relevant for gaining deeper insights into patterns, clusters and relationships among heaps of museum data.
Working with museum big data requires ethical considerations, processes and contexts within both the physical and digital worlds where museum visitors interact. It is only by addressing concerns that are important to visitors and their operations that museums can develop a strategic framework to effectively utilize big data.
Several museums have successfully implemented big data solutions to improve their operations and enhance visitor experiences. For example, the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City used big data to analyze visitor behavior and preferences, which led to the creation of personalized audio guides for visitors.
The British Museum in London used Big Data to optimize staffing levels and reduce wait times for visitors. The National Gallery of Art in Washington DC used big data to analyze visitor feedback and improve the museum’s digital offerings.
Museums Are Adopting Data-Driven Approaches
Museums are increasingly adopting a data-driven approach to improve the visitor experience, attract more footfall and boost revenue. They use various data collection methods such as surveys, focus groups and technology-based approaches like bar codes, electronic tracking and Wi-Fi. This data helps museums train staff, curate desirable exhibitions and optimize their spending. Some museums even integrate data into their exhibits. However, not leveraging analytics could put them at a competitive disadvantage.
The use of hardware-based technology to gather and synthesize data has its drawbacks, especially for non-profit organizations like museums.
According to the American Alliance of Museums (AAM), only a small fraction (10%), of museums in the United States possess budgets that exceed $15 million. On the other hand, a significant percentage of museums (48%) have budgets ranging from $500,000 to $2.9 million.
Most museums have limited budgets and cannot invest heavily in experiential technologies like electronic tracking, Wi-Fi and expensive hardware. Additionally, privacy concerns and the need for a consent-based approach pose significant challenges.
To overcome these hurdles, Mapsted has developed a hardware-free location-based analytics solution that enables museums to leverage data without impacting their revenue. Mapsted’s technology empowers museums to access valuable data that helps them determine the most desirable exhibits and optimize visitor flow to enhance their experience. The platform also allows museums to create data-driven journeys that are more likely to succeed.
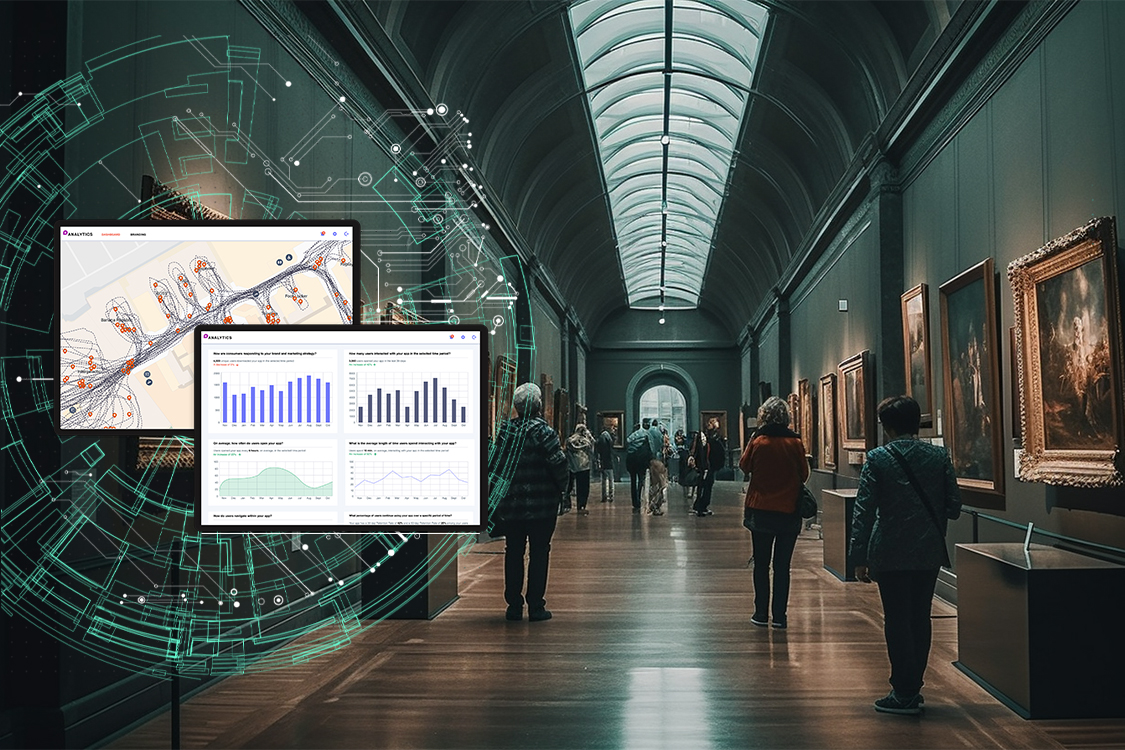
Mapsted’s platform comprises three features that provide valuable insights to museums.
- A user-friendly dashboard visualization feature enables museums to analyze user trajectories, average visit times, footfall heatmaps and path analytics to design a successful journey.
- Real-time reports and insights empower museums to stay in control of operations by taking swift actions on trends the data reveals.
- Predictive Alerts enable museums to anticipate behaviour, intent and potential issues, allowing them to take proactive measures.
Enhancing Museum Experiences With Museum Visitor Analytics
Museums today must embrace digital transformation to stay competitive, relevant and engaging. Museum visitor analytics enables institutions to understand foot traffic, engagement levels and visitor preferences. With this data, museums can design better exhibitions, allocate resources efficiently and improve visitor satisfaction.
Visitor analytics also provides insights into:
- Peak visiting hours: Helps with staff and resource allocation.
- Dwell time analysis: Determines the most engaging exhibits.
- Heatmaps: Show popular areas to optimize exhibit placements.
- Repeat visitor tracking: Helps in tailoring loyalty programs.
By integrating museum analytics, institutions can create more personalized and immersive experiences, ultimately leading to higher engagement and revenue.
How Museum Big Data Supports Strategic Decision-Making
Big data allows museum administrators to make evidence-based decisions by analyzing:
- Visitor demographics: Age, gender, nationality and group size.
- Engagement metrics: Interaction levels with exhibits and displays.
- Marketing effectiveness: Evaluating which campaigns drive attendance.
- Revenue trends: Understanding visitor spending habits on tickets, merchandise and memberships.
For example, if museum attendance data reveals a drop in visitor numbers, organizations can adjust marketing efforts, redesign exhibits or introduce new engagement strategies to boost attendance.
Ultimately, Big Data = Big Gains for Museums and Museum-Goers
The benefits of gathering big data are many. For instance, museums have been:
- Improving the user experience: Big data enables museums to gain a deeper understanding of visitor behaviour, preferences and needs. This understanding can help museums tailor their offerings to better meet visitor expectations.
- Attracting visitors: By analyzing data on visitor demographics, preferences and behaviour, museums can create targeted marketing campaigns to attract new visitors and retain existing ones.
- Driving revenue: By analyzing data on visitor spending patterns, museums can optimize their pricing strategies, create more effective fundraising campaigns and develop new revenue streams.
- Improving operational efficiency: By analyzing data on museum operations, such as visitor flow, exhibit popularity and staffing levels, museums can optimize their resources and improve their overall efficiency.
- Enhancing exhibits: By analyzing data on exhibit popularity, visitor engagement and feedback, museums can optimize their exhibition design and create more compelling and interactive displays.
How To Gather Museum Big Data?
Below are outlined five steps for the collection of big data in museums –
- Identify the data sources. Determine which sources of data are available and relevant to your analysis. This could include visitor records, exhibit data, website analytics, financial records and more.
- Set up data collection systems. To gather data effectively, you’ll need to set up systems that can capture and store the data you need. This might include developing data collection forms, setting up databases or using data analytics tools.
- Analyze the data. Once you have collected the data, you’ll need to analyze it to uncover insights and patterns. This could involve using statistical analysis, data visualization tools or machine learning algorithms.
- Interpret the results. Once you have analyzed the data, you’ll need to interpret the results to understand what they mean for your museum. This could involve identifying areas where you can improve visitor experience, optimize operations or better engage with your audience.
- Take action. Based on your analysis and interpretation of the data, take action to improve your museum. This might involve implementing new programs, changing the layout of exhibits or refining your marketing strategy.
Technology Currently Employed for Collection of Data
- RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology. This is used to track museum objects and monitor visitor movements.
- Visitor feedback systems. These systems collect feedback from visitors through surveys, comment cards or interactive kiosks.
- Web analytics tools. These tools track visitor activity on museum websites and social media platforms.
- Collection management systems. These systems help museums organize and manage their collections, including cataloging and digitization.
- Mobile apps. These apps provide visitors with interactive experiences and can collect data on visitor behavior and preferences.
However, the individual advantages of these technologies are amplified by integrating them with Mapsted location-based technology. Mapsted’s technology is engineered to capture contextual data when users are in proximity to Points of Interest (PoIs) and geofenced areas. This improves the efficacy of the current technologies that museums employ to elevate customer experience, safety and operational efficiency.
Closing Thoughts
The use of big data in museums has become increasingly important in improving the overall visitor experience, attracting more visitors, driving revenue, improving operational efficiency and enhancing exhibits. It has become a crucial tool for museums to remain competitive in today’s digital age.
With Mapsted’s location technology platform, museums can gain valuable insights into visitor behaviour and preferences, optimize resources and create personalized and engaging experiences for their visitors. If you’re considering modernizing museums with Mapsted’s technology, we’ve got some innovative approaches that you should know. Contact Mapsted today and experience patented technology that is pioneering change with a vision. If you enjoyed learning a bit about big data and how it can help your museum, you may be interested in our blog on Ways to Modernize Your Museum and our short video on Maximize Engagement at Your Museum With Location-Based Technology | Mapsted.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is big data in the context of museums?
Ans. Big data in museums refers to the vast amount of data generated from human interactions that impact museums on an hourly or daily basis. This data can include visitor numbers, dwell time, traffic hotspots, social media activity and more.
Q2. What are the key categories of data that drive museum success?
Ans. The key categories of data that drive museum success include visitor data, collection data, operations data, marketing data and social media data.
Q3. How have some museums successfully implemented big data solutions?
Ans. Several museums have successfully implemented big data solutions to improve their operations and enhance visitor experiences. For example, the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City used big data to analyze visitor behavior and preferences, which led to the creation of personalized audio guides for visitors.
Q4. What are the benefits of gathering big data for museums?
Ans. The benefits of gathering big data for museums include improving the user experience, attracting visitors, driving revenue, improving operational efficiency and enhancing exhibits.
Q5. How can museums gather big data without impacting their revenue?
Ans. To gather big data without impacting their revenue, museums can use Mapsted’s location-based analytics solution, which empowers museums to access valuable data that helps them determine the most desirable exhibits and optimize visitor flow to enhance their experience. The platform also allows museums to create data-driven journeys that are more likely to succeed.
Q6: What is museum visitor analytics and why is it important?
A: Museum visitor analytics refers to the process of collecting and analyzing visitor data to improve operations, exhibit design and marketing efforts. It helps museums understand visitor behavior, optimize space usage and enhance engagement.
Q7: What technologies are used for visitor tracking in museums?
A: Some commonly used visitor tracking systems for museums include:
- RFID & NFC tags for tracking visitor movement.
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth beacons for location-based analytics.
- Geofencing technology to monitor exhibit interactions.
- Computer vision and AI-powered cameras for crowd analysis.
Q8: How do museums ensure visitor data privacy while using analytics?
A: Museums must comply with privacy regulations like GDPR and implement data anonymization techniques to protect visitor identities. Secure data storage, fingerprint protection and encrypted geolocation tracking can further enhance security.
Q9: How can big data help museums personalize visitor experiences?
A: By analyzing visitor behavior and preferences, museums can offer:
- Personalized exhibit recommendations
- Customized museum tours based on past visits
- Targeted promotions and loyalty rewards
Q10: How does Mapsted’s technology support museums with data-driven insights?
A: Mapsted’s hardware-free location-based analytics helps museums gain valuable insights into visitor behavior without expensive infrastructure. It provides real-time heat maps, predictive analytics and secure geolocation tracking, allowing museums to optimize visitor flow and engagement.
